Talk Overview
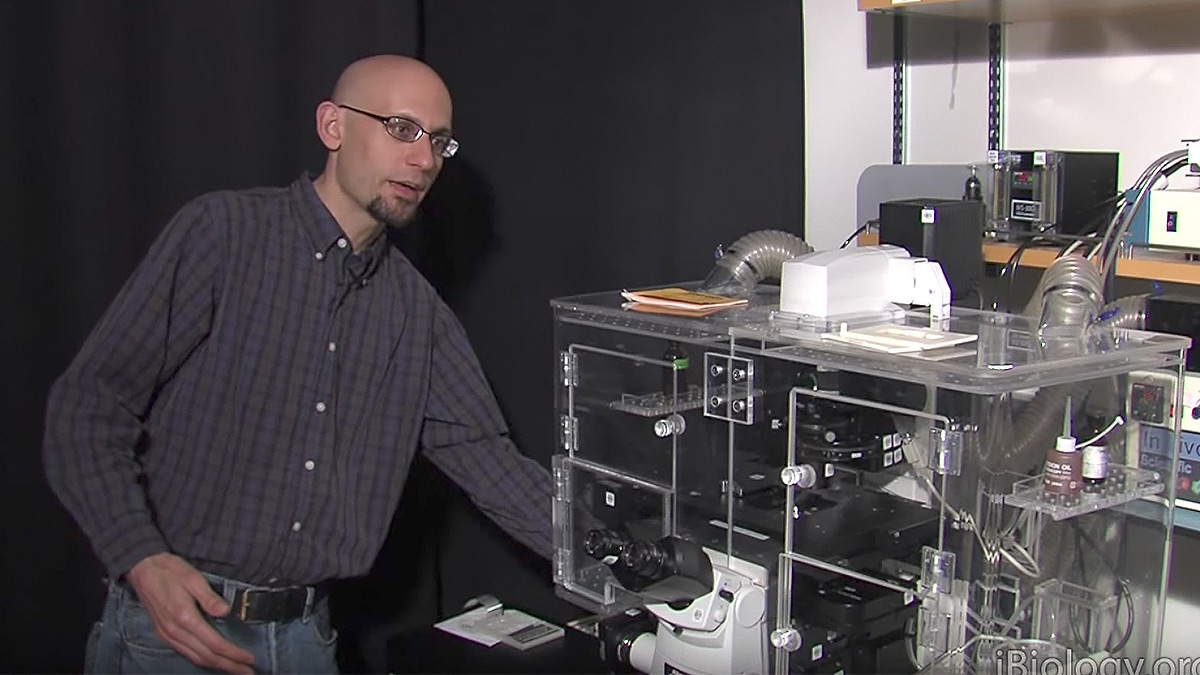
Taking apart a microscope helps you discover all the important optical components and get a better understanding of how things work. It is not always practical to do this yourself, therefore, have a look at this video to see the internals of the Nikon Ti Eclipse microscope.
Questions
- The fluorescence aperture diaphragm:
- Attenuates the intensity of illumination
- Unlike the condenser diaphragm for transmitted light, fluorescence aperture adjustment does not affect resolution
- Is conjugate with the specimen
- A and B
- A, B and C
- True or False. The flange focal distance in an ISO C-mount is standardized so that the primary image plane is located at the camera detector.
- Which of the following are components of the optical nose piece in this Nikon microscope
- Objective lens
- An infrared laser diode for automated focusing
- DIC prisms
- The Bertrand lens
- A and B
- A, B and C
- A, B, C and D
- The field diaphragm in the fluorescence light path
- Is a good location for focusing a laser beam for creating an intense spot of illumination for FRAP (fluorescence recovery after photobleaching)
- Is conjugate with the back focal plane of the condenser
- Is typically located deep within the body of the microscope
- Can be shifted in the optical light path by adjustment with a slider
Answers
View AnswersSpeaker Bio
Steve Ross

Stephen Ross is the General Manager of Product and Marketing at Nikon Instruments. He is also very involved in teaching microscopy at the Marine Biological Laboratory in Woods Hole and at the Bangalore Microscopy Course at the National Centre for Biological Sciences. Continue Reading







Leave a Reply